ist unistall whatever versions you have docker os
docker -v
docker-compose -v
stop the xampp
sudo /opt/lampp/lampp stop
2004 docker-compose up --build
2005 sudo apt-get purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
2006 sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
2007 sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
2008 sudo apt-get autoremove -y
2009 docker -v
2010 docker-compose -v
2011 sudo apt-get remove docker-compose
2012 docker-compose -v
latest laravel
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel my-laravel-app
now install from scratch
before up docekr we have to know docker is there or not
docker -v
docker-compose -v
how to run into mysql bash
and download all the databases
docker exec -it mysql bash
bash-4.2# cd /var/lib/mysql
bash-4.2# mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > /var/lib/mysql/all_databases.sql
Enter password:
bash-4.2# docker cp mysql:/var/lib/mysql/all_databases.sql /path/on/host/all_databases.sql
bash: docker: command not found
bash-4.2# ls
mysql -u root -pSHOW DATABASES
exit from sql bash
docker cp mysql:/var/lib/mysql/all_databases.sql ./all_databases.sql
docker-compose up -d --build
it will call dockerfile then execute .yaml file
docker-compose up -d
it will execute in yaml file
if image is there it will swithc on thatg image
if image is not there it will downloa dthat images
sample docker file
Dockerfile
# Use the official PHP image as base
FROM php:8.0-fpm
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /var/www/html
# Install dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
git \
curl \
libpng-dev \
libonig-dev \
libxml2-dev \
zip \
unzip
# Install PHP extensions
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo_mysql mbstring exif pcntl bcmath gd
sample docker-compose.yml
version: '2'
services:
nginx:
container_name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17
restart: always
ports:
- "9999:9999"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
links:
- php
php:
container_name: php
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
restart: always
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ~:/home
- ./php-config/php.ini:/usr/local/etc/php/php.ini
composer:
container_name: composer
image: composer:latest
command: tail -f /dev/null
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
mysql_testing:
container_name: mysql_testing
image: mysql:5.7
command: mysqld --max-allowed-packet=64M --character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci --init-connect='SET NAMES UTF8;' --innodb-flush-log-at-trx-commit=0
volumes:
# Mount mysl data directory to keep it perisstent on host system.
# Use this only in development environment
# Mysql cannot write to data folder as it is owned by user on host.
# So chown 999:999 data folder when it is first created
#- ~/storage/mysql/log:/var/log/mysql
- ~/storage/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql
environment:
- "MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjw"
- "MYSQL_DATABASE=testing"
- "MYSQL_USER=testing"
- "MYSQL_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjws"
ports:
- "3306:3306"
phpmyadmin_testing:
container_name: phpmyadmin_testing
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
restart: always
environment:
- PMA_HOST=mysql
- PMA_PORT=3306
ports:
- 8000:80
volumes:
- /sessions
nginx/default.conf
server {
listen 9999;
listen [::]:9999;
index index.php index.html;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
root /var/www/testing_docker/public;
client_max_body_size 2048M;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass php:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.(vtt)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
}
}
php-config/php.ini
file_uploads = On
memory_limit = 2048M
max_file_size = 2048M
upload_max_filesize = 2048M
post_max_size = 2048M
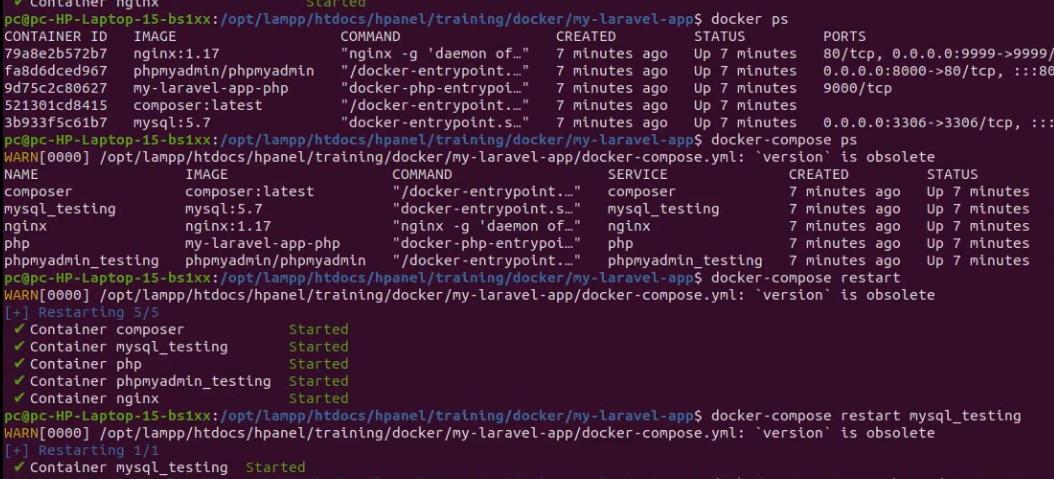
docker ps -a
to know all the containers in present system
docker ps
docker ps
docker images -a
docker images
to know all the images at my system
docker-compose down
docker-compose down -v
to remove the contianers
remove images from system
docker rmi -f $(docker images -q)
kil all the containers
docker kill $(docker ps -q)
docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
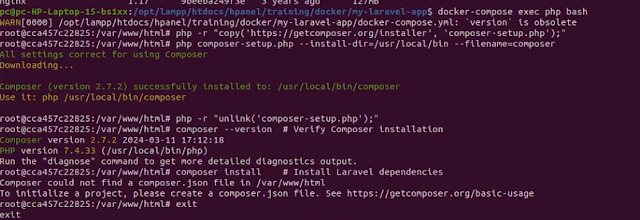
to install composer inside of docker
docker-compose exec php bash
php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
php composer-setup.php --install-dir=/usr/local/bin --filename=composer
php -r "unlink('composer-setup.php');"
composer --version # Verify Composer installation
composer install # Install Laravel dependencies
to tknow the stgatus of docker
docker-compose ps
to know the status of docker-compose
to stop contianers using docker stop
ist stop then remove
docker stop contianer_d container_id
to remove
docker rm container_id contginer_id
to remove images
docker rmi image id
to run inside the container
docker-compose restart
it will restart the containers
docker-compose exec phpmyadmin_testing bash
usign this
we can go intoi phpmyadmin container
cat /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php
remov allthe sql storage dataa
sudo rm -rf ~/storage/mysql/data
to go inside the mysql and chekc the databases
docker-compose exec mysql_Testing mysql -u root -ppassword
create testing user
grant all privilages
flush all privilages
show databases;
show databases;
select user,host, grant_priv frommysql.user where user='root'
how to write docker-compose.yaml file
With Docker version 26.0.0 and Docker Compose version v2.26.1, you should be well-positioned to use Docker Compose file format version 3.x
version: '3'
In a Docker Compose file, the service definitions include various key elements like image, ports, volumes, and depends_on that instruct Docker how to run containers based on those definitions. Here's what each of those elements means in the context of your provided snippet:
image
The image keyword specifies which Docker image to use when creating the container. In your snippet, nginx:latest tells Docker to pull the latest version of the nginx image from Docker Hub if it's not already available locally.
ports
The ports section maps ports from the container to the host machine. The format "80:80" means Docker will map port 80 inside the container to port 80 on your host machine, allowing you to access the nginx server by visiting http://localhost or http://<your-machine-ip> on your web browser.
volumes
Volumes are used to persist data and share directories between the host machine and the container or between containers. In your configuration:
./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf mounts a configuration file from your host machine into the container. This allows you to customize the nginx configuration../html:/usr/share/nginx/html mounts a directory from your host machine to the container where nginx serves static files. This is useful for serving a website or web application.
volumes:
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
- ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html
depends_on
depends_on defines dependencies between services, ensuring that the specified services are started before the current service. In your snippet, it indicates that the web service depends on the php and db services. Docker Compose will start php and db services first. However, it's important to note that depends_on does not wait for php and db to be fully ready (e.g., database to accept connections) before starting web; it merely controls the order of service startup.
This setup is common for web applications where an nginx server serves as a reverse proxy or static file server, relying on PHP for dynamic content generation and a database (db) for data storage.
Creating a docker-compose.yaml file involves defining various services, networks, and volumes that make up your application. Below is a step-by-step guide to writing a basic docker-compose.yaml file. This example will create a simple web application stack with nginx as the web server, php-fpm for PHP processing, and mysql as the database.
Step 1: Specify the Version
Start by specifying the version of the Docker Compose file format. Use a version compatible with your Docker Engine. As of my last update, version 3 is widely used and recommended for most users.
Step 2: Define Services
Services define the containers you want to run. For our web application, we will define three services: web, php, and db.
Define the Web Service
services:
web:
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
- ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html
depends_on:
- php
- db
This service uses the latest nginx image, maps port 80 on the host to port 80 in the container, and mounts two volumes: one for the Nginx configuration and one for the HTML files.
Define the PHP Service
php:
image: php:7.4-fpm
volumes:
- ./php:/usr/share/nginx/html
depends_on:
- db
This service uses the php:7.4-fpm image and mounts a volume for PHP files.
Define the Database Service
db:
image: mysql:5.7
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: rootpassword
MYSQL_DATABASE: mydatabase
MYSQL_USER: user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: password
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
This service uses the mysql:5.7 image, sets environment variables for the MySQL configuration, and uses a named volume to persist database data.
Step 3: Define Volumes
Volumes are used to persist data between container rebuilds and restarts.
volumes is location
Here, db_data is a named volume that will store the MySQL database files.
Step 4: (Optional) Define Networks
If you need to create a custom network for your services, you can define it under the networks key. If not specified, Docker Compose creates a default network for you.
You can then attach services to this network using the networks key under each service.
Complete docker-compose.yaml Example
Combining all the parts, here's what the complete docker-compose.yaml file might look like:
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
- ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html
depends_on:
- php
- db
php:
image: php:7.4-fpm
volumes:
- ./php:/usr/share/nginx/html
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: mysql:5.7
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: rootpassword
MYSQL_DATABASE: mydatabase
MYSQL_USER: user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: password
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
volumes:
db_data:
This file is a basic starting point. Depending on your application's specific needs, you might need to add more services, configure networks differently, or specify more environment variables.
if you wanan run two applications at a time
for all applications common is
php, composer,mysql,phpmyadmin
variable is nginx
nginx:
container_name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17
restart: always
ports:
- "9999:80"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
links:
- php
nginx_two:
container_name: nginx_two
image: nginx:1.17
restart: always
ports:
- "9998:80"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ../location_From_this_file/nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
links:
- php
we hav to change container names otherwise conflicts happen
and ports also
web_two:
container_name: web_two
image: nginx:1.17
ports:
- "81:80"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
node_two:
container_name: node_two
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
volumes:
- '..:/var/www'
command: tail -f /dev/null
ports:
- "8081:8080"
=
version: '3.7'
services:
web:
container_name: web
image: nginx:1.17
ports:
- "94:80"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
node:
container_name: node
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
volumes:
- '..:/var/www'
command: tail -f /dev/null
ports:
- "8094:8094"
unistall docker
sudo apt-get purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
sudo apt-get autoremove -y
install docker
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
sudo docker build -t helloworld
sudo docker run hello-world
docker without sudo
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
codewithmosh.com
what is docker
virtual machines vs containers
architecture of docker
installing docke r
development work flow
what is docker
for example we have xampp server at linux
we can run our larvel or php applications at that server
its ok upto one person but if it is developing by so many developers
if xampp we used, that not same specas in all our developers
because of this we may get errros while executing our code in some other developer system
so for this unique purpose we will run or develop in one system means
we download one image to our local that will also download in other develope r
so its nice to be in allour colleagues one system
docker: one platfoirm for building , running and shipping applications
global
software version mismatch -> all colleaguse same specs lke php verfsion or node version
docker install
docker-compose up -d
thats it to instal;l in new system
if we wann run in same system with different node versions its possible with docker
app1=> node 8
app2 => node 6
down the docke => docker-compose down --rmi all
virtual machine vs contianer
container is isolated enviroment
vitual machiens => we can run so many virtual machines (difrent os ) in one physical applicaiton
macos
hyopervisors
windows
vmware
hyper-v
you can observer if we start our laptop -> it will take time to switch on
and it will ocupu our ram and we can install some vms only in our pc
8gms of memroy => divide for each vms ( finally we can run upto 3 vms)
thats the reason we use containers
docker or containers
lightweight
use os of the host
we can run mltiple apps
it can strt quickly
need less hardware resources
docker architechture
client server architechture
client rest api to server (docekr enginer)
error
Error response from daemon: driver failed programming external connectivity on endpoint mysql_testing (4ea5f2b0ec19e41b12f0dfce908adf5b5df99ad4fda5f9fca30422d84fe5bf1d): Error starting userland proxy: listen tcp4 0.0.0.0:3306: bind: address already in use
sudo netstat -tuln | grep 3306
sudo systemctl stop mysql
sudo systemctl restart docker
sudo service apache2 stop
sudo /opt/lampp/lampp stop
sudo kill `sudo lsof -t -i:3306`
reset the password of phpmyadmin
docker-compose exec mysql_testing mysql -u root -pueDMcQVb8JVCyjw -e "SET PASSWORD FOR 'testing'@'%' = PASSWORD('ueDMcQVb8JVCyjws');"
check the logs of container
docker-compose logs phpmyadmin_testing
how to find compsoer vefrsion
composer show laravel/framework --all | grep versions
docker inspect phpmyadmin_testing
to check connect ot docekr or on
mysqli::real_connect(): php_network_getaddresses: getaddrinfo for mysql failed: Temporary failure in name resolution i
to resolve this error
pma_host name is same as sql container
environment:
- PMA_HOST=mysql_testing
- PMA_PORT=3306
modoified yaml file
version: '2'
services:
nginx:
container_name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17
restart: always
ports:
- "9999:9999"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
links:
- php
php:
container_name: php
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
restart: always
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ~:/home
- ./php-config/php.ini:/usr/local/etc/php/php.ini
composer:
container_name: composer
image: composer:latest
command: tail -f /dev/null
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
mysql_testing:
container_name: mysql_testing
image: mysql:5.7
command: mysqld --max-allowed-packet=64M --character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci --init-connect='SET NAMES UTF8;' --innodb-flush-log-at-trx-commit=0
volumes:
# Mount mysl data directory to keep it perisstent on host system.
# Use this only in development environment
# Mysql cannot write to data folder as it is owned by user on host.
# So chown 999:999 data folder when it is first created
#- ~/storage/mysql/log:/var/log/mysql
- ~/storage/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql
environment:
- "MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjw"
- "MYSQL_DATABASE=testing"
- "MYSQL_USER=testing"
- "MYSQL_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjws"
ports:
- "3306:3306"
networks:
- mynetwork
phpmyadmin_testing:
container_name: phpmyadmin_testing
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
restart: always
environment:
- PMA_HOST=mysql_testing
- PMA_PORT=3306
ports:
- 8000:80
volumes:
- /sessions
networks:
- mynetwork
networks:
mynetwork:
driver: bridge
now iam getting
SQLSTATE[HY000] [2002] php_network_getaddresses: getaddrinfo for mysql_testing failed: Temporary failure in name resolution
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=mysql_testing
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=testing
DB_USERNAME=testing
DB_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjws
php and mysql_testing not connected to same network
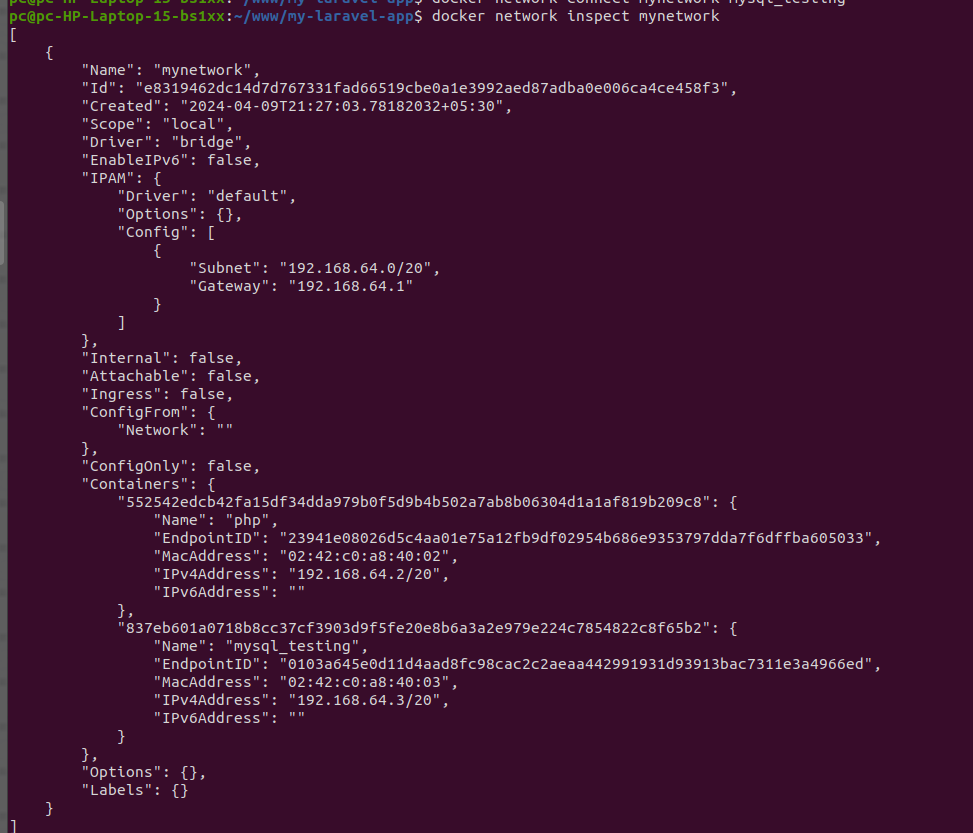
docker network create --driver bridge mynetwork
docker network inspect mynetwork
docker network connect mynetwork php
docker network connect mynetwork mysql_testing
docker network inspect mynetwork
docker-compose exec composer composer dump-autoload -o
./dock php php artisan migrate
now vuejs part
vue create frontend
vue3
docker-compose up -d --build
./dock node npm run serve
docker exec -it node /bin/bash
npm install
docker-compose build
docker-compose up
docker-compose build --no-cache
sudo lsof -i :80
docker exec -it node npm cache clean --force
docker exec -it node npm install
install signle package
npm install -D @vue/compiler-sfc
docker exec -u 1000:1000 -w /var/www/frontend -it your_container_name /bin/bash
docker exec -it node node -v
npm -v
docker exec -it node npm -v
v12.7.0
pc@pc-HP-Laptop-15-bs1xx:~/www/frontend$ docker exec -it node /bin/bash
root@ec1818eaa417:/var/www# node -v
v12.7.0
root@ec1818eaa417:/var/www# npm -v
6.10.0
root@ec1818eaa417:/var/www#
docker exec -it node /bin/bash
npm list vue @vue/compiler-sfc
npm install vue@^3.2.13 @vue/compiler-sfc
npm cache clean --force
sudo chmod -R 777 storage/logs
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2TOEtV85uA
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S6-qKbT8RLo
VUE
nginx/default.conf
server {
root /var/www/frontend/dist;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}
dock
#!/bin/bash
# This is a helper script to run a command on docker container from host machine
# Usage: ./dock container_name command_to_run param1 param2 param3
# This script assumes user has followed below conventions
# 1. User has home folder like /home/svs
# 2. User has all web projects inside /home/svs/www
# 3. User has mounted /home/svs/www to /var/www on docker container
# User home directory is mapped to /var on docker container. Modify as required.
# Example: HOST:/home/svs => CONTAINER:/var
# Any subfolders like www are mapped automatically
# Example: HOST:/home/svs/www/project => CONTAINER:/var/www/project
MAP_HOST_DIR="${HOME}"
MAP_CONTAINER_DIR="/var"
#########################
# Do not edit below this
#########################
# Modify container name and working directory as required
container_name="$1"
# Validate if container name is passed
if [ -z "${container_name}" ] ;
then
echo -e "Missing container_name"
echo -e "Usage: ${0} container_name command_to_run param1 param2 param3\n"
exit 1
fi
# Validate if container name is valid docker container
if [ "$(docker inspect -f '{{.State.Running}}' ${container_name})" != "true" ] ;
then
echo -e "Docker container '${container_name}' is not running"
echo -e "\nList of running Docker containers:"
docker ps --format '{{.Names}}'
echo -e "\n"
exit 1
fi
# Validate if atleast simple command is passed as $2
if [ -z "${2}" ] ;
then
echo -e "Missing command to run on docker container"
echo -e "Usage: ${0} container_name command_to_run param1 param2 param3\n"
exit 1
fi
# Map host working dir to container working dir
host_working_dir="${PWD}"
# echo "${host_working_dir}"
container_working_dir="${host_working_dir/$MAP_HOST_DIR/$MAP_CONTAINER_DIR}"
# Ensure container working dir starts with mapped container dir to avoid accidental execution in unwanted folders
if [[ $container_working_dir != ${MAP_CONTAINER_DIR}* ]] ;
then
echo "Failed to execute docker command"
echo "Container working dir must start with '${MAP_CONTAINER_DIR}'"
echo "Container working dir resolved to '${container_working_dir}'"
fi
# echo "${container_working_dir}"
# Command to run. We forward all params to this script to actual command
COMMAND="$2 $3 $4 $5 $6 $7 $8 $9 ${10}"
# We login into container as current user UID and run command
# We set GID to be same as UID
GID=${UID}
# echo "${COMMAND}"
# exit 0
# Run command
docker exec -u ${UID}:${GID} -w ${container_working_dir} -it ${container_name} ${COMMAND}
=
docker-compose.yml
version: '3.7'
services:
web:
container_name: web
image: nginx:1.17
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
node:
container_name: node
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
volumes:
- '..:/var/www'
command: tail -f /dev/null
ports:
- "8080:8080"
=
Dockerfile
FROM node:lts
WORKDIR /var/www/
RUN npm install vue@^3.2.13
RUN npm install @vue/cli@4.5.0 -g
=
laravel
nginx/default.conf
server {
listen 9999;
listen [::]:9999;
index index.php index.html;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
root /var/www/my-laravel-app/public;
client_max_body_size 2048M;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass php:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.(vtt)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
}
}
=
php-config/php.ini
file_uploads = On
memory_limit = 2048M
max_file_size = 2048M
upload_max_filesize = 2048M
post_max_size = 2048M
===
dock
#!/bin/bash
# This is a helper script to run a command on docker container from host machine
# Usage: ./dock container_name command_to_run param1 param2 param3
# This script assumes user has followed below conventions
# 1. User has home folder like /home/svs
# 2. User has all web projects inside /home/svs/www
# 3. User has mounted /home/svs/www to /var/www on docker container
# User home directory is mapped to /var on docker container. Modify as required.
# Example: HOST:/home/svs => CONTAINER:/var
# Any subfolders like www are mapped automatically
# Example: HOST:/home/svs/www/project => CONTAINER:/var/www/project
MAP_HOST_DIR="${HOME}"
MAP_CONTAINER_DIR="/var"
#########################
# Do not edit below this
#########################
# Modify container name and working directory as required
container_name="$1"
# Validate if container name is passed
if [ -z "${container_name}" ] ;
then
echo -e "Missing container_name"
echo -e "Usage: ${0} container_name command_to_run param1 param2 param3\n"
exit 1
fi
# Validate if container name is valid docker container
if [ "$(docker inspect -f '{{.State.Running}}' ${container_name})" != "true" ] ;
then
echo -e "Docker container '${container_name}' is not running"
echo -e "\nList of running Docker containers:"
docker ps --format '{{.Names}}'
echo -e "\n"
exit 1
fi
# Validate if atleast simple command is passed as $2
if [ -z "${2}" ] ;
then
echo -e "Missing command to run on docker container"
echo -e "Usage: ${0} container_name command_to_run param1 param2 param3\n"
exit 1
fi
# Map host working dir to container working dir
host_working_dir="${PWD}"
# echo "${host_working_dir}"
container_working_dir="${host_working_dir/$MAP_HOST_DIR/$MAP_CONTAINER_DIR}"
# Ensure container working dir starts with mapped container dir to avoid accidental execution in unwanted folders
if [[ $container_working_dir != ${MAP_CONTAINER_DIR}* ]] ;
then
echo "Failed to execute docker command"
echo "Container working dir must start with '${MAP_CONTAINER_DIR}'"
echo "Container working dir resolved to '${container_working_dir}'"
fi
# echo "${container_working_dir}"
# Command to run. We forward all params to this script to actual command
COMMAND="$2 $3 $4 $5 $6 $7 $8 $9 ${10}"
# We login into container as current user UID and run command
# We set GID to be same as UID
GID=${UID}
# echo "${COMMAND}"
# exit 0
# Run command
docker exec -u ${UID}:${GID} -w ${container_working_dir} -it ${container_name} ${COMMAND}
===
docker-compose.yml
services:
nginx:
container_name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17
restart: always
ports:
- "9999:9999"
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ./nginx/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
links:
- php
php:
container_name: php
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
restart: always
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
- ~:/home
- ./php-config/php.ini:/usr/local/etc/php/php.ini
composer:
container_name: composer
image: composer:latest
command: tail -f /dev/null
volumes:
- ../:/var/www
mysql_testing:
container_name: mysql_testing
image: mysql:5.7
command: mysqld --max-allowed-packet=64M --character-set-server=utf8 --collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci --init-connect='SET NAMES UTF8;' --innodb-flush-log-at-trx-commit=0
volumes:
# Mount mysl data directory to keep it perisstent on host system.
# Use this only in development environment
# Mysql cannot write to data folder as it is owned by user on host.
# So chown 999:999 data folder when it is first created
#- ~/storage/mysql/log:/var/log/mysql
- ~/storage/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql
environment:
- "MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjw"
- "MYSQL_DATABASE=testing"
- "MYSQL_USER=testing"
- "MYSQL_PASSWORD=ueDMcQVb8JVCyjws"
ports:
- "3306:3306"
networks:
- mynetwork
phpmyadmin_testing:
container_name: phpmyadmin_testing
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
restart: always
environment:
- PMA_HOST=mysql_testing
- PMA_PORT=3306
ports:
- 8000:80
volumes:
- /sessions
networks:
- mynetwork
networks:
mynetwork:
driver: bridge
===
Dockerfile
# Use the official PHP image as base
FROM php:8.2-fpm
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /var/www/html
# Install dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
git \
curl \
libpng-dev \
libonig-dev \
libxml2-dev \
zip \
unzip
# Install PHP extensions
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo_mysql mbstring exif pcntl bcmath gd
===
Hello Docker!
docker run hello-world
Experience the magic of Docker with the simplest container ever
2/ Run a Web Server
docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginx
Fire up a web server on port 8080 from the official NGINX image.
3/ Dockerize your App
docker build -t myapp .
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 myapp
Package your app into a Docker image and run it on port 3000.
4/ Persistent Data
docker volume create mydata
docker run -d -v mydata:/app/data myapp
Persist data outside the container with Docker volumes.
5/ Link Containers
docker network create mynet
docker run -d --network mynet --name db postgres
docker run -d --network mynet --name app myapp
6/ Multi-Container App
Docker Compose:
Define services in docker-compose.yml.
docker-compose up -d
Orchestrate multiple containers effortlessly
7/ Inspect Containers
docker ps
docker inspect <container_id>
Dive deep into container details for troubleshooting and analysis.
8/ Container Logs
docker logs <container_id>
Access real-time logs to monitor container behavior.
9/ Container Lifecycle
docker start <container_id>
docker stop <container_id>
Manage container lifecycle with simple commands.
10/ Container Exec
docker exec -it <container_id> bash
Enter the container's shell for debugging or maintenance.
11/ Build Optimization
Leverage Dockerfile best practices like layer caching for faster builds.
12/ Docker Registry
docker push <image_name>
docker pull <image_name>
Store and share images securely on Docker Hub or private registries.
3/ Scaling Services
Docker Swarm: docker swarm init
docker service scale <service_name>=<replica_count>
Scale your application horizontally with Docker Swarm.
14/ Health Checks
HEALTHCHECK instruction in Dockerfile.
Ensure container health and auto-restart on failure.
15/ Docker Security
Follow security best practices like image scanning, least privilege, and Docker Content Trust (DCT) to secure your containerized environment.
How does Docker work?
The diagram below shows the architecture of Docker and how it works when we run “docker build”, “docker pull” and “docker run”.
There are 3 components in Docker architecture:
 Docker client
The docker client talks to the Docker daemon.
Docker client
The docker client talks to the Docker daemon.
 Docker host
The Docker daemon listens for Docker API requests and manages Docker objects such as images, containers, networks, and volumes.
Docker host
The Docker daemon listens for Docker API requests and manages Docker objects such as images, containers, networks, and volumes.
 Docker registry
A Docker registry stores Docker images. Docker Hub is a public registry that anyone can use.
Let’s take the “docker run” command as an example.
1. Docker pulls the image from the registry.
2. Docker creates a new container.
3. Docker allocates a read-write filesystem to the container.
4. Docker creates a network interface to connect the container to the default network.
5. Docker starts the container.
Docker registry
A Docker registry stores Docker images. Docker Hub is a public registry that anyone can use.
Let’s take the “docker run” command as an example.
1. Docker pulls the image from the registry.
2. Docker creates a new container.
3. Docker allocates a read-write filesystem to the container.
4. Docker creates a network interface to connect the container to the default network.
5. Docker starts the container.
https://twitter.com/i/status/1779175580824707178
===




















docker exec -it mysql_testing mysql -uroot -pueDMcQVb8JVCyjw (docker exec -it mysql_testing mysql -uroot -p
ReplyDeleteUPDATE mysql.user SET host='%' WHERE user='root' AND host='localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;)
docker exec -it ping .
ReplyDeletedocker exec -it php ping mysql_testing
OCI runtime exec failed: exec failed: unable to start container process: exec: "ping": executable file not found in $PATH: unknown