https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1rm5T40Wsjo
synchronous and asynchrnous
script.js
console.log("fist0ln");
console.log("secondln");
it have to execute first line then only it execute second line
till ist line execute it will not go to next line
synchronous or blocking code
asynchronouse or non blocking code
console.log("fist0ln");
setTimeout(()=>{},2000);
console.log("secondln");
setTimeout(()=>{},2000);
()=>{} ist one is function or argument
second one is time or seconds
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
},2000);
below is the programm
console.log("fist0ln");
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
},2000);
console.log("secondln");
output of above programm is
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3ZY_sqGszDI
fistline
secondline
getting data from database
it will execute ist line then
it will call next, it tolda i will excute after 2 seconds
then its not blocking
its excute next line second line
fist line
immedietely next line
afer 2 seconds databsae line
restarnt syste
we have ktichen and two tables
boy takes order from table 1, went to kichen till not ready the table one order
it will not go to second table
that is blocking or synchronous
non-blicking
takes order from table one and told to kitchen
then go to table 2, told to kitchen
he is not watiing tll order is ready
programm 3
console.log('firstline');
const student = getData();
console.log(student);
console.log('last line');
function getData(){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
return {name:"bob",id:1};
},2000);
}
result is
firstline
undefined
lastline
how to print the data from datbase
in asyncrhonouse
we use 3 mehtods
callbacks , primises, async or await
call back -> it is a function which is excuted after another functioin has finished execution
any function that we passed as an argument to another function , s o we call that function is called call back functioin
means
we are passing function as an argumetn
after finished eecution of main , it will execute later
programm 3
console.log('firstline');
const student = getData('1');
console.log(student);
console.log('last line');
function getData(id){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
return {name:"bob",id:id};
},2000);
}
above there is no confusion just return from argument
now we are passsing one more argument is function
console.log('firstline');
getData('1',(student)=>{console.log("student",student)});
console.log('last line');
function getData(id,callback){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
callback( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
}
()=>{}
processing in curly brackets
() => arguemnts in c brackets
first it print
first line
then it calls getdata it told i will print after 2 seconds
print second line
then getingdata from database
then {}
now we are not getting undefined, b
settimeout first arguemtn is function , second arguemtn is seconds
programm -4
console.log('firstline');
getData('1',
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,(subjects)=>{
console.log(subjects);
})
}
);
console.log('last line');
function getData(id,callback){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
callback( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
}
function getsubjects(id,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("gettingsubjects of student",id);
callback(["maths","science"]);
},2000);
}
ist it print firstline
then it call get data withargument and call back
when it reach to call back
it call getsubjects
firstline
call , it told wait 2 seconds
cal it told wait 2 seconds
last line
firstline
lastline
gettingdatafromdatabase
{name:"bob
after 2 seconds
gettingsubjects of stude
["maths","s

programm 5
console.log('firstline');
getData('1',
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,(subjects)=>{
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],(marks)=>{
console.log(marks)
})
})
}
);
console.log('last line');
function getData(id,callback){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
callback( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
}
function getsubjects(subject,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("gettingsubjects of student",subject);
callback(["maths","science"]);
},2000);
}
function getmarks(mark,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting marks",mark);
callback([1,2]);
},2000);
}
callback function
function calls another function
it calls anotehr function
multiple callbacks
called callback hell
programm 5
console.log('firstline');
getData('1',
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,(subjects)=>{
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],(marks)=>{
console.log(marks)
})
})
}
);
console.log('last line');
function getData(id,callback){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
callback( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
}
function getsubjects(subject,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("gettingsubjects of student",subject);
callback(["maths","science"]);
},2000);
}
function getmarks(mark,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting marks",mark);
callback([1,2]);
},2000);
}
below is anonymouse function
(marks)=>{
console.log(marks)
})
becauase it has no name
so namin gthis function
getData('1',
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,(subjects)=>{
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],(marks)=>{
console.log(marks)
})
})
}
);
modifying above
(marks)=>{
console.log(marks)
})
to
function displaymarks(marks){
console.log(marks)
}
getData('1',
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,(subjects)=>{
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],displaymarks(marks))
})
}
);
modifying below
(subjects)=>{
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],displaymarks(marks))
}
displaySubjects (subjects){
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],displaymarks(marks))
}
getData('1',
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,displaySubjects(subjects))
}
);
nw modifting below
(student)=>{
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,displaySubjects(subjects))
}
displaystudents(student){
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,displaySubjects(subjects))
}
programm -6
console.log('firstline');
getData('1',
displaystudents(student)
);
console.log('last line');
function displaystudents(student){
console.log("student",student);
getsubjects(student.id,displaySubjects(subjects))
}
function displaySubjects (subjects){
console.log(subjects);
getMarks(subjects[0],displaymarks(marks))
}
function displaymarks(marks){
console.log("marks",marks)
}
function getData(id,callback){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
callback( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
}
function getsubjects(subject,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("gettingsubjects of student",subject);
callback(["maths","science"]);
},2000);
}
function getmarks(mark,callback){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting marks",mark);
callback([1,2]);
},2000);
}
promise
it will hold the result of ayncrhonouse operatioon or
promise is promise you to give you the result of the asyncrhonouse operation or give you error
with promise
it will give error or result ( it will defenetley geive one output)
new promise();
ist one is resolve next one is reject
()=>{}
new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
const student={id:20,name:"bob"};
resolve(student);
},2000);
})
promise.
before inition of promise is in intiated state
then once statedd async and completed the oprationit comes under fullfilled state
once not completed it comes under rejected state
if promise is resolved then i s fullflled
after that stora the datea to one varaibvle
promise/then((result)=>{console.log(result});
new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
const student={id:20,name:"bob"};
resolve(student);
},2000);
})
promise.then((result)=>{console.log(result});
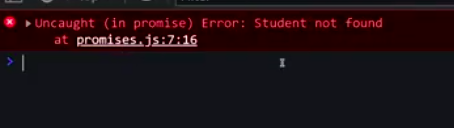
new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
reject(new Error('steudent not found'));
},2000);
})
promise
.then((result)=>{console.log(result)})
.catch((error)=>{ console.log(error)});
programm=7
function getData(id,callback){
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
callback( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
}
console.log('firstline');
const promise= getData(1);
promise.then((student) => console.log(student));
function getData(id){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
resolve( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
});
}

convert remaining functions into promises
const promise= getData(1);
promise
.then((student) => getsubjects(student.id))
.then(subjects => getMarks(subjects[0]))
.then(mark => console.log(mark))
.catch(error => console.log(error))
;
function getData(id){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
resolve( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
});
}
function getsubjects(subject){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("gettingsubjects of student",subject);
resolve(["maths","science"]);
},2000);
});
}
function getmarks(mark){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting marks",mark);
resolve([1,2]);
},2000);
});
}
async -await
getstudent(1)
it return promise
so
const student= await getData(1);
const subjects= await await getsubjects(student.id);
const mark= await getMarks(subjects[0]);
consoile.log(mark);
function displayData(){
const student= await getData(1);
const subjects= await await getsubjects(student.id);
const mark= await getMarks(subjects[0]);
consoile.log(mark);
};
if we are using await
we have to use async
async function displayData(){
const student= await getData(1);
const subjects= await await getsubjects(student.id);
const mark= await getMarks(subjects[0]);
console.log(mark);
};
displayData();
function getData(id){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout (()=>{
console.log("getting data from database");
resolve( {name:"bob",id:id});
},2000);
});
}
function getsubjects(subject){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("gettingsubjects of student",subject);
resolve(["maths","science"]);
},2000);
});
}
function getmarks(mark){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("getting marks",mark);
resolve([1,2]);
},2000);
});
}
if we write like this
async function displayData(){
const student= await getData(1);
const subjects= await await getsubjects(student.id);
const mark= await getMarks(subjects[0]);
console.log(mark);
};
our javascript engine will convert to syncrhonous code
const promise= getData(1);
promise
.then((student) => getsubjects(student.id))
.then(subjects => getMarks(subjects[0]))
.then(mark => console.log(mark))
.catch(error => console.log(error))
;
how can we show error in below
async function displayData(){
const student= await getData(1);
const subjects= await await getsubjects(student.id);
const mark= await getMarks(subjects[0]);
console.log(mark);
};
using try and catch
async function displayData(){
try{
const student= await getData(1);
const subjects= await await getsubjects(student.id);
const mark= await getMarks(subjects[0]);
console.log(mark);
}
catch(error)
{
console.log(error);
}
};
async loadComponent() {
this.isComponentLoaded = false; // Set to false to show suspense
// Simulate an asynchronous component load
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 2000));
this.currentComponent = () => import('./MyComponent.vue');
this.isComponentLoaded = true;
},
in synchrnous javascript
without execution of first line
it wil not go to second line
in asynchronous also
async function (){
const var_one = await function_name();
const var_onee = await sfunction_name();
}
withut executing ist line it is not going to second line
whats the use of async
In both synchronous and asynchronous JavaScript, the order of execution is crucial. In synchronous code, each line of code is executed in sequence, and the program waits for each line to complete before moving to the next one. This means that if the first line is not executed, the second line won't be executed either.
For example, in synchronous code:
const var_one = someFunction();
console.log(var_one);
In the above code, console.log(var_one) won't execute until someFunction() completes its execution because JavaScript is single-threaded and synchronous by default.
Now, when it comes to asynchronous code, things work a bit differently. The async keyword is used to define asynchronous functions. An asynchronous function can contain await expressions, which pause the execution of the function until a promise is resolved. This allows asynchronous code to execute non-blocking operations.
For example, in asynchronous code:
async function fetchData() {
const var_one = await someFunction();
console.log(var_one);
}
fetchData();
In this case, await someFunction() will pause the execution of fetchData() until someFunction() completes and the promise it returns is resolved. Once resolved, var_one will be assigned the result, and then console.log(var_one) will be executed.
The async keyword and await expressions are useful in asynchronous programming because they allow you to write code that looks synchronous while handling asynchronous operations in a more readable and manageable way. This is especially beneficial when dealing with tasks like fetching data from APIs, reading files, or performing other I/O operations that may take some time to complete.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nAokVuQzuxA4vqrRb5PWm6wyJlApjTql/view?ref=morioh.com
=====







No comments:
Post a Comment